A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
W
White Matter
Pronunciation: WITE MA-ter
Definition: White matter consists of bundles of myelinated axons that connect various gray matter areas (the processing centers) of the brain to each other and to the spinal cord. Its characteristic white appearance is derived from myelin, a lipid-rich insulating sheath produced by oligodendrocytes. Functionally, white matter facilitates the rapid transmission of action potentials via saltatory conduction, allowing for synchronized neural activity across long distances. In nootropic research, white matter integrity is viewed as the "bandwidth" of the brain, directly correlating with processing speed and executive coordination.
The Nootropic Research Interface
Research into white matter focuses on "Structural Connectivity," emphasizing the preservation and repair of the myelin sheath to maintain signal fidelity.
- Myelination and Repair: The thickness and health of the myelin sheath determine the speed of the electrical signal. Nootropics that provide phospholipid precursors—such as Citicoline, Phosphatidylserine, and Omega-3 fatty acids (DHA)—are studied for their ability to support oligodendrocyte health and the structural maintenance of white matter tracts.
- Fractional Anisotropy (FA): This is a primary metric used to measure the "health" of white matter. It tracks the directional flow of water molecules along axons. Nootropics that reduce neuroinflammation, such as Longvida Curcumin, are researched for their ability to prevent the "fraying" of these tracts, thereby maintaining high FA values in aging populations.
- White Matter Hyperintensities (WMH): These are small lesions in white matter often caused by chronic low-level vascular issues. Research into Vasotropics (like Ginkgo Biloba) focuses on preserving the micro-circulation that feeds the deep white matter, preventing the "disconnectivity" that leads to age-related cognitive decline.
- Inter-hemispheric Communication: The largest white matter structure is the Corpus Callosum, which allows the left and right hemispheres to communicate. Nootropics that enhance white matter integrity can improve "bilateral integration," which is critical for complex tasks like creative problem-solving and rapid linguistic processing.
White Matter vs. Gray Matter
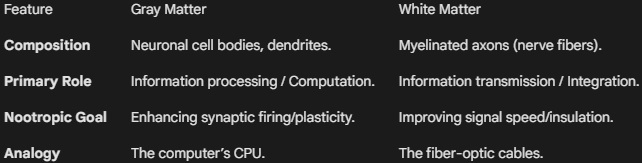
Primary Research Metrics
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI): An advanced MRI technique used to map the orientation and integrity of white matter tracts in vivo. It is the gold standard for seeing how a nootropic intervention affects the brain's "wiring."
- Conduction Velocity: The speed at which an electrical impulse travels along an axon. Increases in conduction velocity are a direct indicator of improved myelination.
- Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell (OPC) Count: A cellular metric used in pre-clinical research to determine if a compound is stimulating the "birth" of new myelin-producing cells.
Research Note: While gray matter often gets the most attention in nootropic circles (due to its link to "thinking"), the White Matter determines how well those "thoughts" are coordinated. A "White Matter Stack" is often considered a long-term investment; unlike the immediate effects of a stimulant on gray matter activity, structural changes to white matter occur over months of consistent nutritional and lifestyle support.
Working Memory
Pronunciation: WUR-king MEM-uh-ree
Definition: Working memory (WM) is a limited-capacity system responsible for the simultaneous storage and manipulation of information. It acts as the "mental scratchpad" required for complex cognitive tasks such as language comprehension, learning, and reasoning. According to the Baddeley-Hitch Model, WM consists of a "Central Executive" that controls the flow of information to two sub-systems: the Phonological Loop (verbal) and the Visuospatial Sketchpad (visual). In nootropic research, WM is considered the single best predictor of fluid intelligence (Gf).
The Nootropic Research Interface
Research into WM-enhancement focuses on increasing the "computational bandwidth" of the prefrontal cortex (PFC).
- The Dopaminergic "Gating": The ability to hold information in WM without being distracted is controlled by dopamine levels in the Prefrontal Cortex. Nootropics that modulate D1 receptor activity (like Bromantane or Modafinil) are researched for their ability to "gate" the entry of information into the workspace, preventing the system from becoming overloaded by noise.
- Persistent Neuronal Firing: Unlike long-term memory, WM depends on the continuous firing of neurons in the PFC. Nootropics that support Mitochondrial ATP or modulate HCN channels (like Guanfacine in clinical research) help maintain this high-energy firing state, effectively increasing the "size" of the mental scratchpad.
- Acetylcholine and Signal Clarity: Acetylcholine is essential for the "resolution" of the data held in WM. Researchers use Alpha-GPC or Coluracetam to sharpen the contrast of mental images or verbal strings, making them easier for the Central Executive to manipulate.
- The N-Back Threshold: Nootropic efficacy is often measured by a subject's ability to move from a "2-back" to a "3-back" task. This transition represents a significant leap in the brain's ability to discard old data and update the workspace with new variables in real-time.
Working Memory vs. Short-Term Memory

Primary Research Metrics
- N-Back Task: The gold-standard test where a subject must identify if a current stimulus matches one presented "n" steps ago. It measures the dynamic updating of the WM buffer.
- Operation Span (OSPAN): A test requiring the subject to solve math problems while simultaneously remembering words, measuring the "multitasking" capacity of the Central Executive.
- Theta-Gamma Coupling: An EEG biomarker; the "nesting" of gamma waves within theta waves is thought to represent the physical mechanism of how different "items" are held in the working memory workspace.
Research Note: Working memory is highly sensitive to Stress and Cortisol. High cortisol levels cause dopamine to flood the PFC, which actually "shuts down" working memory (the "brain freeze" effect). Nootropics that act as Adaptogens (like Rhodiola Rosea) are valued for their ability to protect working memory capacity under high-pressure conditions.
