Index:
Complete Technical Specifications
- General Identification
- Chemical & Physical Properties
- Radiological Specifications
- Binding Affinity (Ki Values)
- Pharmacokinetics & Metabolism
- Radiation Dosimetry (mGy per 185 MBq)
- Clinical Outcomes & Safety
Complete History
- Pre-Clinical Origins: The Phenyltropane Foundation (1980s–1990)
- Development of FP-CIT: The Birth of Ioflupane (1991–1995)
- Clinical Validation & European Launch (1996–2000)
- The Long Road to FDA Approval (2000–2011)
- Expansion into Dementia & Recent History (2011–2026)
Research Information
- Molecular Pharmacology & Binding Affinity
- Kinetic Modeling & Distribution
- Radiochemistry & Decay Characteristics
- Pharmacological Interference Registry
- Dosimetry & Safety Research
Striatal Binding Ratio (SBR)
- The Fundamental SBR Equation
- Region of Interest (ROI) Analysis
- Kinetic Modeling: The Binding Potential (BP)
- Partial Volume Effect (PVE) Correction
- Factors Affecting the Calculation
Landmark Clinical Research Ledger
- Benamer et al. (2000)
- Catafau et al. (2004)
Complete Technical Specifications
01. General Identification
- Generic Name: Ioflupane I-123
- Trade Name: DaTscan
- Pharmacological Class: Phenyltropane; Diagnostic Radiopharmaceuticals
- ATC Code: V09AB03
- CAS Number: 155798-07-5
- PubChem CID: 132999
- UN Number: UN2915 (Radioactive material)
- Canonical SMILES: COC(=O)[C@@H]1[C@H]2CC
C@H - InChI Key: XKWGZCHYIUKXJS-YNSXUUMBSA-N
02. Chemical & Physical Properties
- IUPAC Name: methyl (1R,2S,3S,5S)-8-(3-fluoropropyl)-3-(4-iodophenyl)-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2-carboxylate
- Molecular Formula: C18H23FINO2
- Molecular Weight: 427.28 g/mol
- Exact Mass: 427.08153 g/mol
- LogP: 3.4
- Polar Surface Area: 29.5 square angstroms
- Rotatable Bonds: 5
03. Radiological Specifications
- Radionuclide: Iodine-123
- Production Method: Cyclotron
- Decay Mode: Electron Capture
- Decay Product: Stable Tellurium-123
- Physical Half-Life: 13.2 hours
- Gamma Energy Peak: 159 keV
- X-Ray Emissions: 27 to 32 keV
04. Binding Affinity (Ki Values)
- Dopamine Transporter (DAT): 0.62 nM
- Serotonin Transporter (SERT): 11 nM
- Norepinephrine Transporter (NET): 36 nM
05. Pharmacokinetics & Metabolism
- Blood-Brain Barrier: High permeability (Passive diffusion)
- Brain Uptake: 7 percent of dose within 10 minutes
- Imaging Peak: 3 to 6 hours post-injection (Striatal/Background equilibrium)
- Metabolism: Primarily N-dealkylation and ester hydrolysis
- Urine Excretion: 60 percent within 48 hours
- Fecal Excretion: 14 percent within 48 hours
06. Radiation Dosimetry (mGy per 185 MBq)
Target Organ Absorbed Dose (mGy)
- Bladder Wall: 0.10
- Striatum: 0.041
- Liver: 0.052
- Lungs: 0.043
- Kidneys: 0.036
- Thyroid: 0.018 (requires blocking agent)
Effective Dose: 4.35 mSv
07. Clinical Outcomes & Safety
- Sensitivity: 97 percent for Parkinsonian Syndrome differentiation
- Specificity: 88 percent for Lewy Body Dementia differentiation
- Interfering Drugs: Cocaine, Amphetamines, Methylphenidate, Bupropion, Mazindol, Benztropine, Fentanyl
- Pre-treatment: Thyroid blocking (Potassium Iodide) 1 hour prior to injection
- Contraindications: Pregnancy; Known hypersensitivity to Iodine
- Lactation: Suspend breastfeeding and discard milk for 72 hours post-administration
Complete History
01. Pre-Clinical Origins: The Phenyltropane Foundation (1980s–1990)
The history of Ioflupane begins with the search for high-affinity ligands that could map the brain's dopamine system without the rapid metabolism seen in earlier tracers.
- The Cocaine Template: Researchers began with the structure of cocaine, which naturally binds to the dopamine transporter. However, cocaine's binding is too transient and its affinity too low for effective imaging.
- The WIN Series: Scientists at Sterling-Winthrop developed a series of synthetic phenyltropane analogs. One significant breakthrough was the compound WIN 35,065-2, which proved to be significantly more potent than cocaine.
- Rational Design: In the late 1980s, the goal shifted to creating a "probe" that could be labeled with a radioisotope. By modifying the N-methyl group of the tropane ring with a fluoropropyl group and adding an iodine atom to the phenyl ring, chemists created FP-CIT (the chemical precursor to Ioflupane).
02. Development of FP-CIT: The Birth of Ioflupane (1991–1995)
- Molecular Refinement: The addition of the N-omega-fluoropropyl group was the critical historical pivot. It increased the molecule's lipophilicity, allowing it to cross the blood-brain barrier rapidly, and it improved the "washout" time from non-target areas of the brain.
- Radiolabeling Choice: Researchers chose Iodine-123 over Carbon-11 because Iodine-123 has a 13.2-hour half-life.
This allowed the drug to be manufactured in a central cyclotron and shipped to hospitals, rather than requiring an on-site cyclotron. - The "Neumeyer" Era: Significant work was conducted by Dr. John Neumeyer and colleagues, who demonstrated that 123I-FP-CIT had a superior "signal-to-noise" ratio in the striatum compared to previous ligands like beta-CIT.
03. Clinical Validation & European Launch (1996–2000)
- Once the molecule was stabilized, GE Healthcare (then Amersham Health) moved it into human trials to address a specific clinical need: the inability to distinguish Parkinson’s Disease from Essential Tremor.
- 1999–2000 European Approval: After successful Phase III trials involving 158 patients across Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) granted marketing authorization for DaTscan in July 2000.
- The Benamer Study (2000): This year marked the publication of the seminal research by Benamer et al., which proved the drug had a 97% sensitivity in detecting the loss of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinsonian syndromes.
04. The Long Road to FDA Approval (2000–2011)
- While Europe was using DaTscan throughout the 2000s, the United States path was complicated by the FDA's strict requirements for "clinical impact"—proving not just that the scan was accurate, but that it actually changed how doctors treated patients.
- The CUPS Trial (2004): To satisfy regulators, the "Clinically Unclear Parkinsonian Syndromes" (CUPS) study was conducted. It showed that in 72% of cases, a physician changed their management plan after seeing a DaTscan.
- FDA Approval (January 14, 2011): The FDA finally approved 123I-Ioflupane for use in the U.S. to visualize striatal dopamine transporters in adult patients with suspected Parkinsonian syndromes.
05. Expansion into Dementia & Recent History (2011–2026)
The last 15 years have seen the application of Ioflupane expand from movement disorders into cognitive disorders.
- Lewy Body Dementia (DLB): In 2017, the FDA expanded the indication to include help in distinguishing Dementia with Lewy Bodies from Alzheimer’s Disease. Because DLB involves the loss of dopamine neurons and Alzheimer's typically does not, the scan became a vital differential tool.
- Supply Chain Evolution: Historically, supply was fragile due to the short half-life (13.2h). However, the expansion of high-energy cyclotron networks in the early 2020s stabilized global availability.
- Current Standing (2026): Ioflupane remains the most widely used SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) agent for dopamine transporter imaging. While PET (Positron Emission Tomography) tracers are being developed, Ioflupane's historical data set and logistical ease make it the industry benchmark.
Research Information
1. Molecular Pharmacology & Binding Affinity
Research identifies Ioflupane as a cocaine-analog phenyltropane.
- Affinity Constants (Ki):
- DAT: 0.62 nM (Ultra-high affinity, providing the "signal").
- SERT (Serotonin): 11 nM (Allows for secondary binding in the raphe nuclei).
- NET (Norepinephrine): 36 nM (Negligible binding at clinical doses).
- Target Site: Specifically binds to the SLC6A3 protein.
- Mechanism: Ioflupane reversibly binds to the reuptake pump. In neurodegenerative states like Parkinson’s Disease, the density of these pumps decreases, resulting in a visible "loss of signal" on SPECT scans.
2. Kinetic Modeling & Distribution
The "extreme detail" of Ioflupane research centers on how the molecule moves through the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) and localizes in the striatum.
- Lipophilicity: LogP of 3.4 allows for rapid passive diffusion across the BBB.
- Uptake Kinetics: Approximately 7% of the injected dose reaches the brain within 10 minutes.
- The SOR Model: Research utilizes the Striatal-to-Occipital Ratio (SOR). Because the occipital cortex has negligible DAT density, it serves as the "background" or "reference" value to calculate the specific binding in the caudate and putamen.
- Equilibrium: Optimal imaging occurs 3 to 6 hours post-injection, when the ratio between specific binding (striatum) and non-specific binding (background) is at its peak.
3. Radiochemistry & Decay Characteristics
The research utility of Ioflupane is tied to the specific physics of the Iodine-123 isotope.
- Isotope: Iodine-123 ($^{123}$I).
- Decay Mode: Electron Capture.
- Energy Peak: 159 keV (Optimal for Gamma Camera detection).
- Physical Half-Life: 13.2 hours.
- Daughter Isotope: Stable Tellurium-123.
- Production: Cyclotron-produced via proton bombardment of Xenon-124.
04. Pharmacological Interference Registry
Extensive research has identified specific "nootropic" and pharmaceutical compounds that compete for the DAT binding site, potentially causing "false positive" results.
- Strong Interference (Must stop 1-7 days prior): Cocaine, Amphetamines, Methylphenidate, Mazindol.
- Moderate Interference: Bupropion (Wellbutrin), Fentanyl, and certain selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) with high DAT affinity (like Sertraline at high doses).
- No Significant Interference: L-Dopa, Pramipexole, Selegiline, and Anticholinergics.
5. Dosimetry & Safety Research
Ethical research requires precise tracking of radiation absorbed by the body (per 185 MBq dose).
- Effective Dose: 4.35 mSv.
- Bladder Wall: 0.10 mGy (Highest exposure organ; mitigated by hydration).
- Striatum: 0.041 mGy.
- Liver: 0.052 mGy.
- Thyroid: 0.018 mGy (Requires pre-administration of Potassium Iodide to block the uptake of free iodine).
Striatal Binding Ratio (SBR)
01. The Fundamental SBR Equation
The SBR is a ratio that compares the density of the tracer in the target area to a reference area that contains no dopamine transporters (usually the occipital cortex).
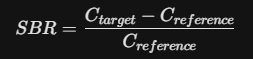
- C_target: The mean radioactive count (concentration) in the Striatum (Caudate or Putamen).
- C_reference: The mean radioactive count in the Occipital Cortex (the "background").
By subtracting the reference count from the target count, you isolate the Specific Binding. Dividing by the reference count again normalizes the data, accounting for differences in the amount of tracer injected or the patient’s individual metabolism.
02. Region of Interest (ROI) Analysis
In research, "Extreme Detail" requires segmenting the Striatum into its sub-structures, as dopamine loss typically follows a specific pattern (starting in the posterior putamen).
- Putamen SBR: Calculated to detect early-stage Parkinsonian symptoms.
- Caudate SBR: Calculated to assess cognitive decline and late-stage progression.
- Asymmetry Index (AI): A mathematical comparison between the left and right hemispheres.

- Significance: A high AI (>10%) is a hallmark of idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease, which usually begins unilaterally.
03. Kinetic Modeling: The Binding Potential (BP)
The SBR is essentially a simplified version of the Binding Potential (BPND) used in PET imaging. In research-grade kinetic modeling, we assume a "Simplified Reference Tissue Model" (SRTM).
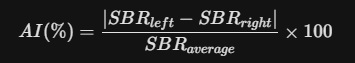
- B_max: Total density of available Dopamine Transporters.
- K_d: The dissociation constant (inversely related to the 0.62 nM affinity).
- f_nd: The free fraction of the tracer in the non-specific compartment.
Because Ioflupane reaches a "pseudo-equilibrium" between 3 and 6 hours, the SBR at that time-point is considered an accurate surrogate for the true BPND.
04. Partial Volume Effect (PVE) Correction
A major hurdle in Ioflupane research is the Partial Volume Effect. Because the Striatum is a small structure, the limited resolution of SPECT cameras causes some "signal spill-over" into surrounding tissues.
Advanced researchers apply a Recovery Coefficient (RC):
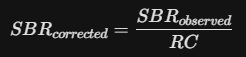
This correction is vital when comparing data across different centers or different camera types to ensure the "Analog Vault" data remains standardized.
05. Factors Affecting the Calculation
To keep the math "clean," the following variables must be stabilized:
- Age-Correction: DAT density naturally declines by approximately 6–7% per decade. Research models must use age-matched controls.
- Specific Binding Ratio vs. Striatal Binding Ratio: While often used interchangeably, the Specific Binding Ratio is the technically broader term, while SBR is the clinical standard for DaTscan.
- Partial Occupancy: If a subject has taken a nootropic like Methylphenidate, the "Available B_max" decreases, artificially lowering the SBR.
06. Technical Summary Table
| Metric | Purpose | Abnormal Threshold |
| Mean SBR | Overall DAT density | < 1.5 (varies by camera) |
| Putamen/Caudate Ratio | Pattern of loss | < 1.0 (indicates PD) |
| Asymmetry Index | Unilateral vs Bilateral | > 10% |
| Background Noise | Image Quality Check | High noise = Lower SBR precision |
Landmark Clinical Research
| Study | Focus | Critical Research Outcome |
| Benamer et al. (2000) | Differential Diagnosis | Demonstrated 97% sensitivity and 100% specificity in distinguishing Parkinsonian Syndromes (PS) from Essential Tremor (ET). |
| Catafau et al. (2004) | Clinical Utility (CUPS) | Proved that Ioflupane SPECT changed the clinical management in 72% of patients with "unclear" tremors. |
| McKeith et al. (2007) | Dementia (DLB) | Established that DAT loss is a core biomarker for Dementia with Lewy Bodies, showing 88% specificity vs. Alzheimer's. |
| Volkow et al. | Cognitive Correlation | Found that striatal DAT density (measured via Ioflupane) correlates with performance on executive function and working memory tasks. |
| Hauser et al. (2011) | Diagnostic Confidence | Showed that scan results significantly increased physician confidence in diagnosis (P < 0.001) in prospective trials. |
Recent Research Frontiers (2020-2026)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Using deep learning to quantify the "SBR" (Striatal Binding Ratio) automatically, reducing human error in interpretation.
- Progression Tracking: Longitudinal research exploring whether the rate of DAT decline can predict the speed of cognitive or motor failure in Parkinson's patients.
- Multi-Tracer Studies: Combining Ioflupane (presynaptic) with 18F-DOPA (enzymatic activity) to create a "3D" map of dopamine health.
